慢病毒整合稳定细胞株
▏ 名词定义
慢病毒:慢病毒是一种逆转录病毒,属于逆转录病毒科。慢病毒表达逆转录酶和整合酶,前者将病毒RNA转化为双链DNA,后者将病毒DNA插入宿主DNA,会随宿主细胞一起分裂。这一特性可用于将各种基因、突变或治疗药物稳定地递送到细胞中,几十年来已在研究界得到广泛应用。一般认为,逆转录病毒只感染分裂细胞,而慢病毒则同时感染分裂细胞和非分裂细胞。
野生型慢病毒已被改造成可在实验室环境中安全使用的慢病毒载体。这些改造的慢病毒载体具有诸多优势,使其成为多种细胞类型和模型中有用的研究工具。慢病毒载体可以靶向非分裂细胞,能够在宿主细胞中长期稳定表达,并且具有较低的免疫原性。
慢病毒载体: 慢病毒的完整基因组通常8-10kb,由单链RNA编码,包含诸多元件,但是实验用于包装的慢病毒,出于安全性的考虑,许多元件都被突变、移除。
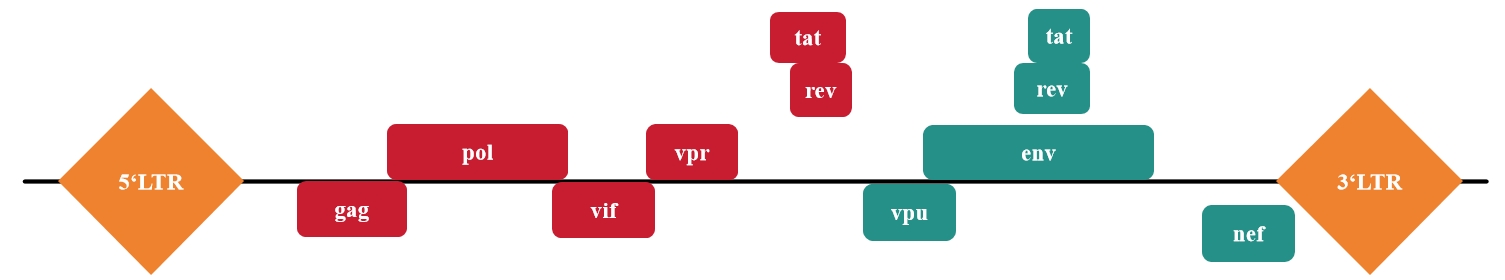
图1 慢病毒的完整基因组元件图示
1. 包装基因包含:gag、pol、env
2. 调控基因包含:tat、rev
3. 辅助基因包含:vif、vpr、vpu、nef
|
Transfer plasmid |
LTR |
in cis |
Long terminal repeat; comprised of a U3-R-U5 structure and are found on each side of the provirus. The U3 (unique 3’) contains sequences necessary for activation of viral genomic RNA transcription. R is the repeat region. |
|
U3 |
in cis |
Unique 3’; contains sequences necessary for activation of viral genomic RNA transcription. Removal of this region in the 3’ LTR in third-generation plasmids creates self-inactivating viral vectors. |
|
|
R |
in cis |
Repeat region where Tat binds. |
|
|
TAR |
in cis |
Trans-activating response element; found in the R region and acts as the binding site for Tat. |
|
|
U5 |
in cis |
Unique 5'; in third-generation plasmids, this region is often removed in 5’ LTRs and replaced with a heterologous promoter (CMV or RSV). |
|
|
5' LTR |
in cis |
Acts as an RNA pol II promoter; the transcript begins, by definition, at the beginning of R, is capped, and proceeds through U5 and the rest of the provirus. Third-generation plasmids use a hybrid 5' LTR with a constitutive promoter such as CMV or RSV. |
|
|
3' LTR |
in cis |
Terminates transcription started by 5' LTR by the addition of a polyA tract just after the R sequence. |
|
|
WPRE |
in cis |
Woodchuck hepatitis virus post‐transcriptional regulatory element; stimulates the expression of transgenes via increased nuclear export. |
|
|
RRE |
in cis |
Rev Response Element; he sequence to which the Rev protein binds. |
|
|
Psi (?) |
in cis |
RNA packaging signal; recognized by nucleocapsid proteins and essential for efficient viral packaging. |
|
|
cPPT |
in cis |
Central polypurine tract; recognition site for proviral DNA synthesis. Increases transduction efficiency and transgene expression. |
|
|
Packaging plasmid |
gag |
in trans |
Precursor structural protein of the lentiviral particle containing matrix, capsid, and nucleocapsid components. |
|
pol |
in trans |
Precursor protein containing reverse transcriptase and integrase components. |
|
|
rev |
in trans |
Binds to the Rev Response Element (RRE) within unspliced and partially spliced transcripts to facilitate nuclear export. Provided by a separate plasmid from gag/pol in third-generation packaging plasmids. |
|
|
tat |
in trans |
Trans-activator; binds TAR to activate transcription from the LTR promoter. Only in first- and second-generation lentiviral plasmids. |
|
|
Envelope plasmid |
env |
in trans |
The viral envelope gene; typically vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein (VSV-G), an envelope protein with broad tropism used to pseudotype most lentiviral vectors. |
▏ 慢病毒载体的演变
第一代质粒包括(图2):
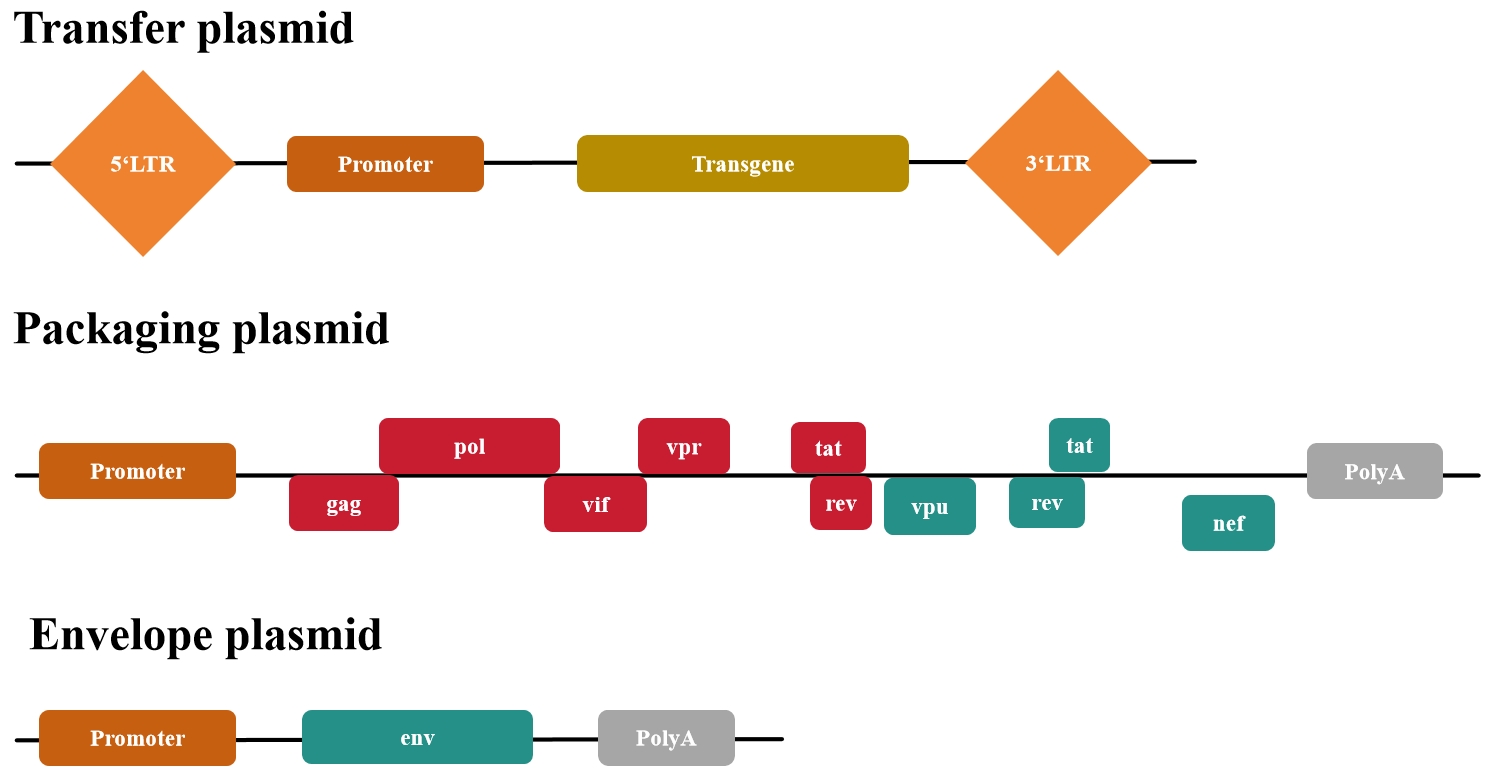
图2 第一代慢病毒质粒系统
第一代慢病毒质粒缺乏安全性改进以及无法生产具有复制能力的慢病毒(即产生能够感染细胞并进一步自我复制的病毒颗粒),基本已经废弃使用了。

第二代质粒包括(图3):
1.转移质粒——含有转基因和野生型 LTR
2.包装质粒— 包含gag、pol、tat和rev
3.包膜质粒— 含有env
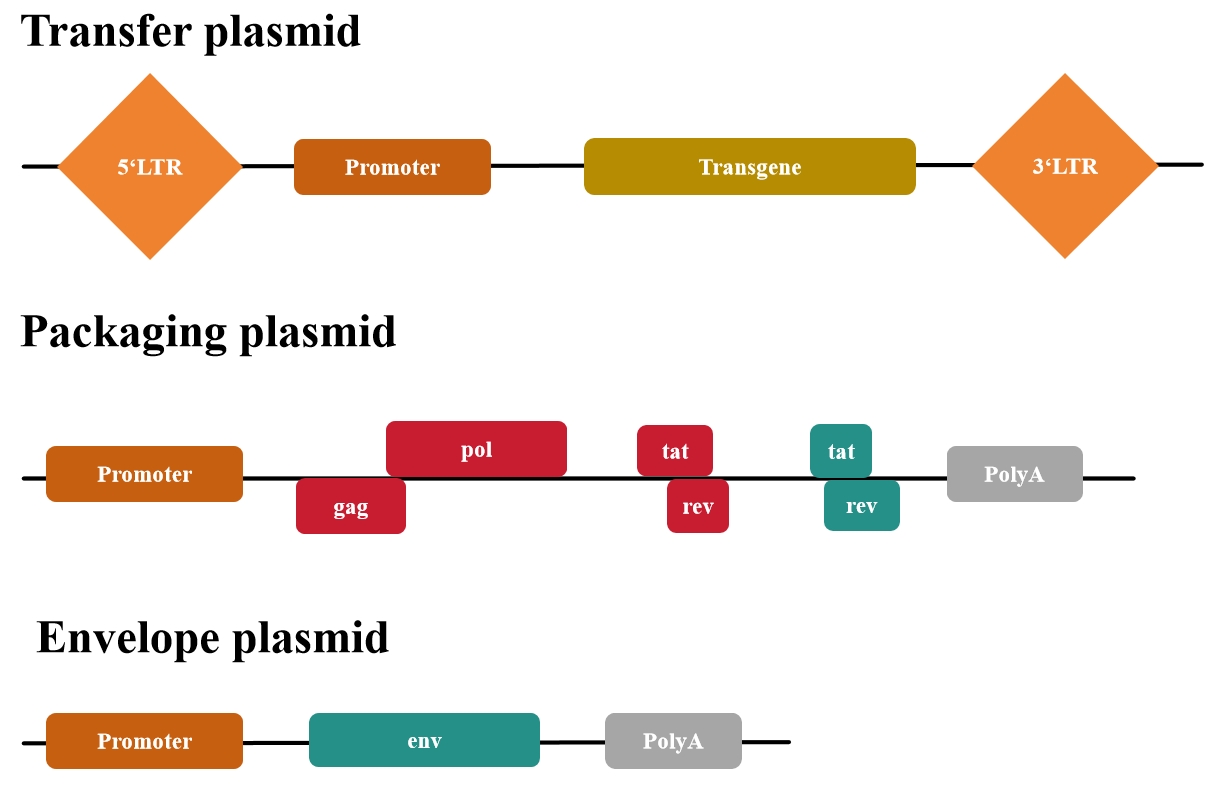
图3 第二代慢病毒质粒系统

第三代质粒包括(图4):
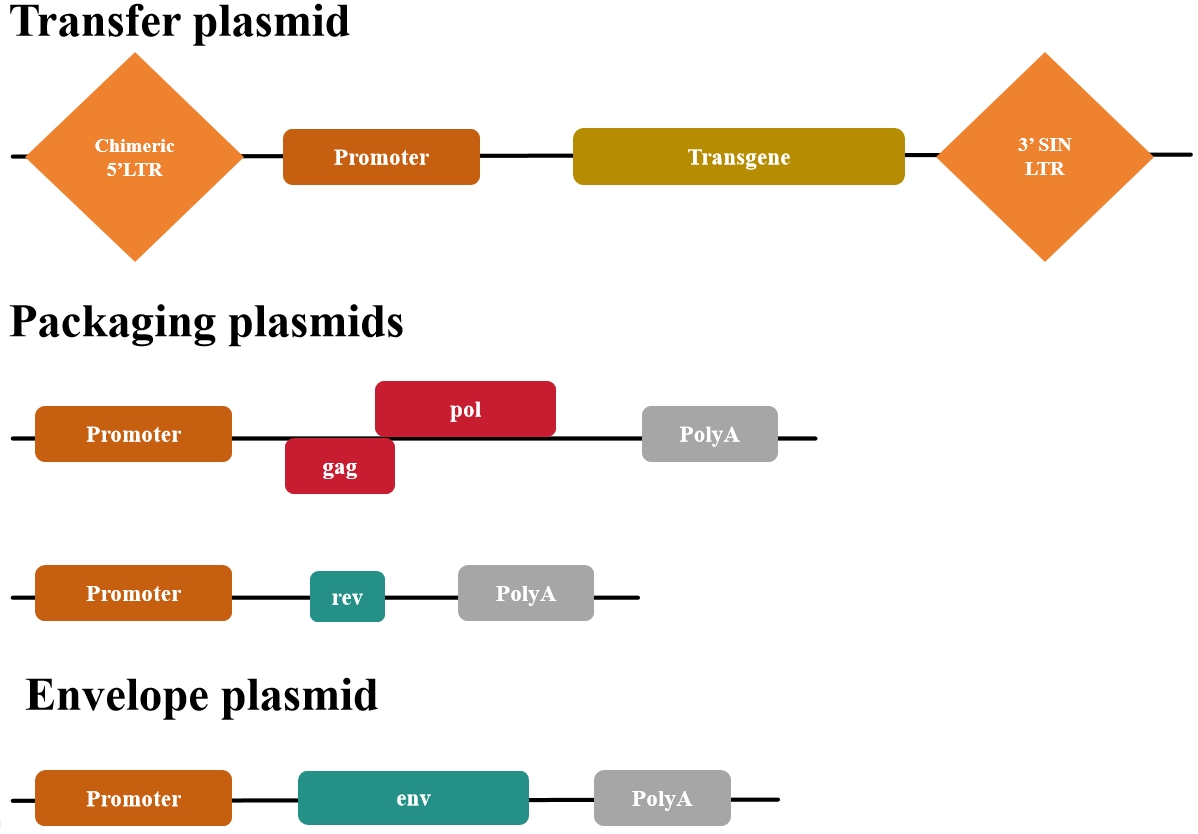
图4 第三代慢病毒质粒系统
大多数第三代转移质粒也含有3' LTR的缺失,使其具有自失活性(SIN)。该缺失在一轮逆转录后转移到5' LTR,从而抑制病毒整合到宿主基因组后全长病毒的转录。这种情况在第二代转移质粒中也常见。

第四代质粒包括(图5):
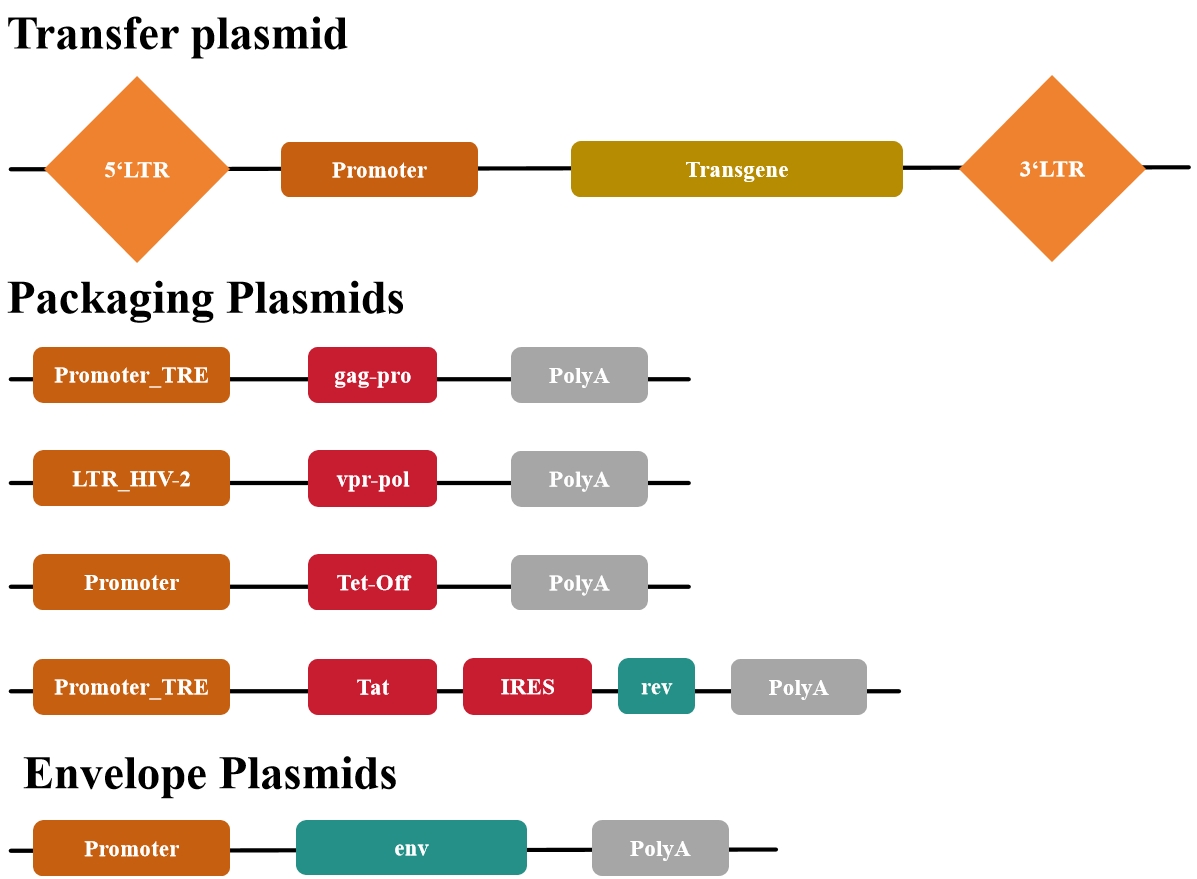
图5 第四代慢病毒质粒系统
第四代包装系统针对病毒产量、易用性和安全性进行了优化。首先系统采用了四环素(Tet系统启动子)转录激活表达,其次同样也采用了Tat反式激活因子驱动病毒的必需成份的高表达,第三gap-pro和vpr-pol被分离到两个质粒上,这次生产复制型慢病毒需要三次低频重组,更安全。而滴度,有报道称,可以达到5*10e8 IFU/mL(未浓缩上清)。
综上,经过历代的慢病毒载体的演变升级,现有的第四代包装系统成为主流的实验室慢病毒包装系统,不管是安全性,还是产量,都是比较有保障的。
▏ 包装的宿主细胞
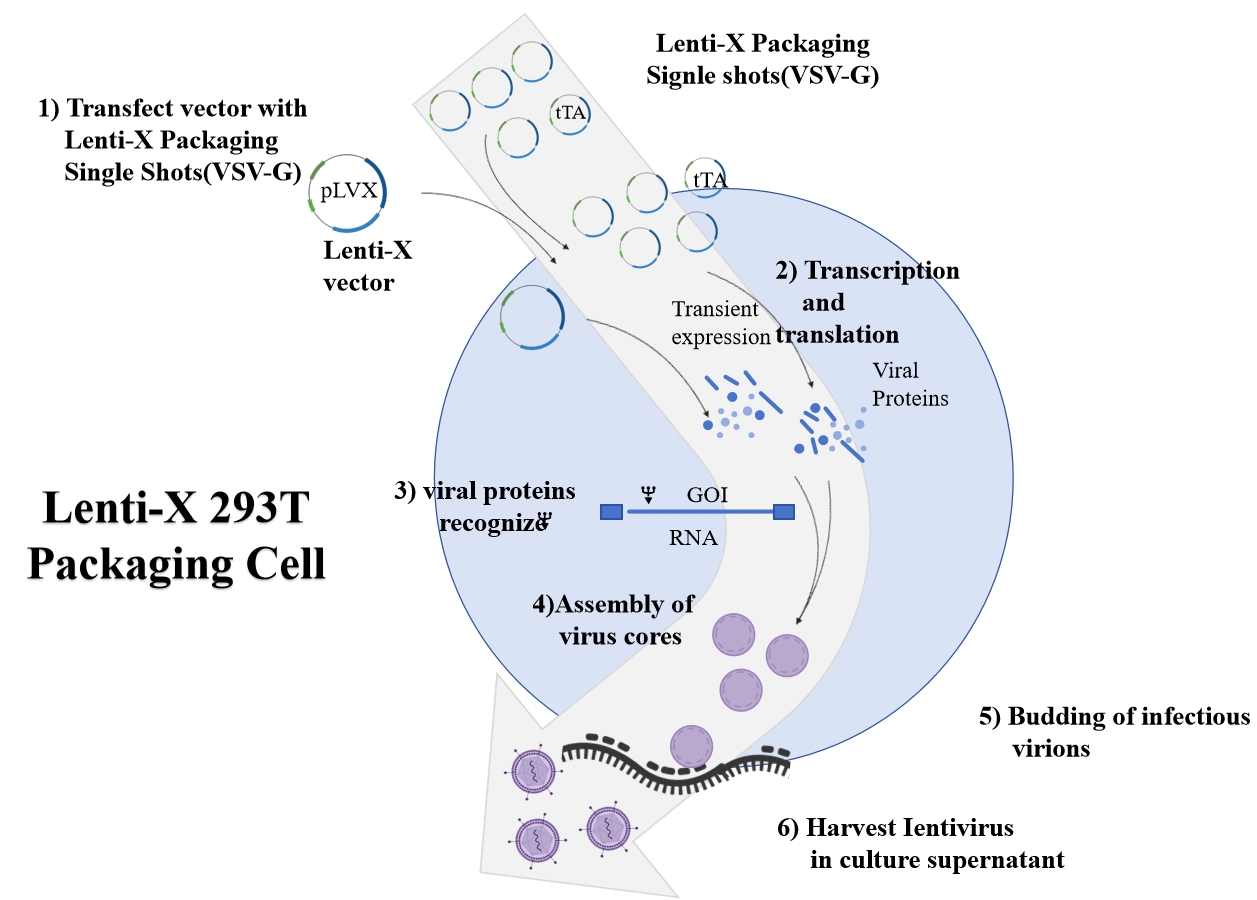
图6 慢病毒包装图示
▏ 纯化和浓缩
▏ 滴度的检测
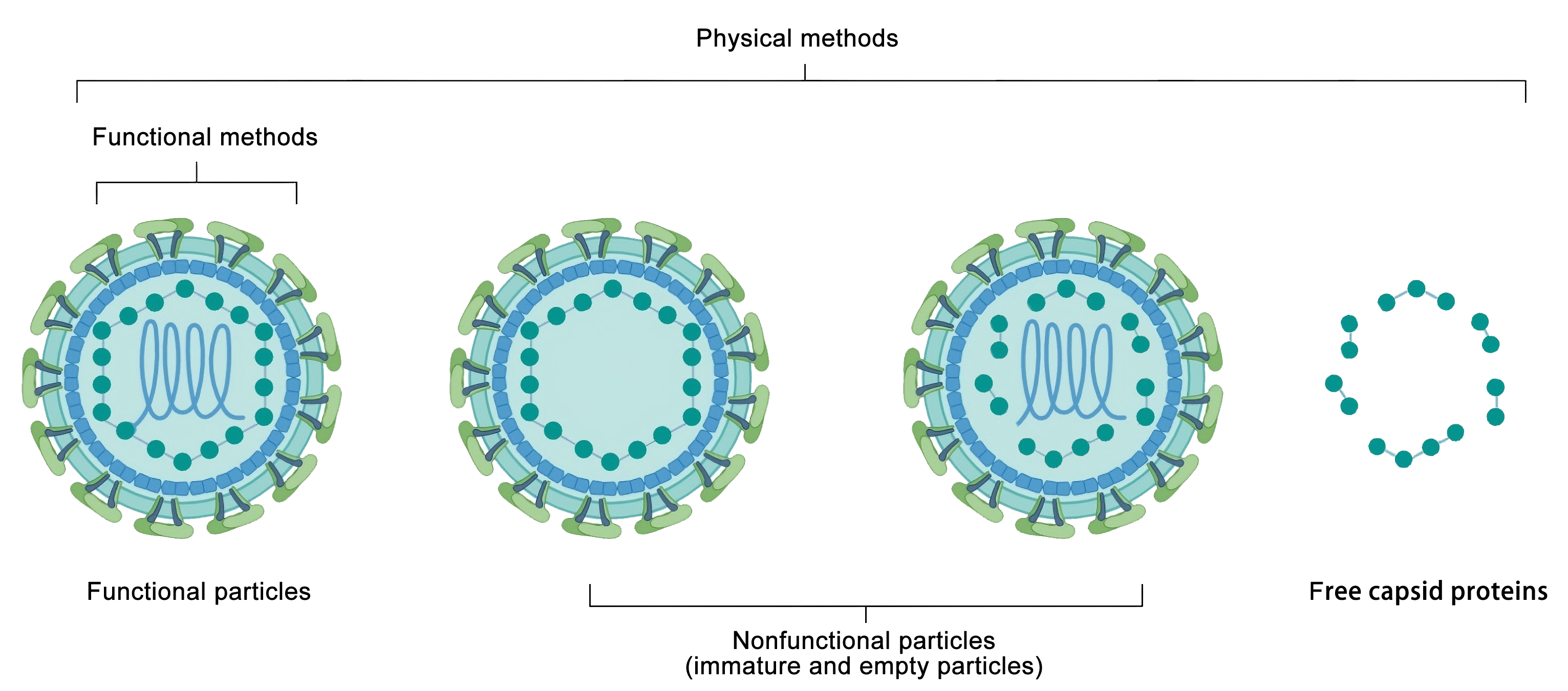

图7 慢病毒包装上清液中存在的产物。物理方法可以测量上清液中释放的功能性和非功能性颗粒,以及游离衣壳蛋白(例如 p24)。功能性滴定方法专门测量功能性病毒颗粒。
▏ 感染靶点细胞
慢病毒(LV)是一种有包膜的病毒,最常见的是VSV-G,它通过与特定的细胞表面蛋白(比如LDLR)结合,随后进行膜融合进入细胞,将含有其遗传信息的病毒RNA注入细胞质。这种单链病毒RNA通过逆转录转化为DNA。病毒DNA进入细胞核,并通过病毒整合酶整合到宿主细胞基因组中。
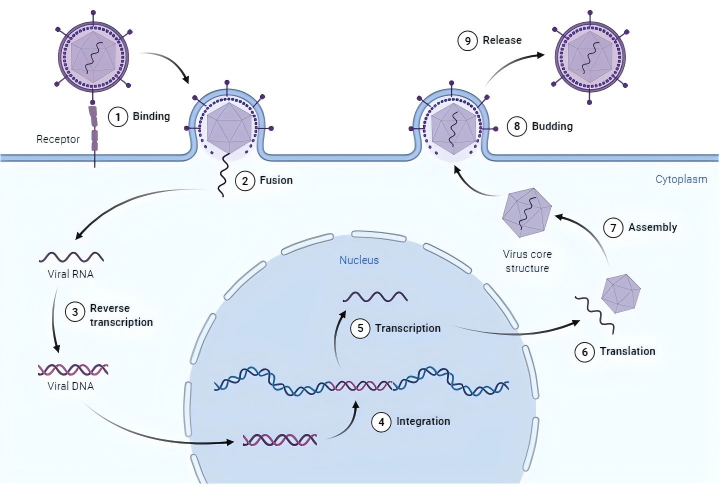
图8 慢病毒整合宿主基因组的图示
▏ 实验中的关键考虑因素
▏ 稳定细胞株构建服务
科佰生物提供“慢病毒整合系统”稳定细胞株构建服务,利用该系统,我们已经成功构建超过900株稳定细胞株的模型,有着丰富的经验,欢迎沟通咨询。
|
|
质粒转染 |
病毒感染 |
Flp-FRT系统 |
转座子系统 |
基因编辑 |
||
|
脂质体 |
电转 |
慢病毒 |
|||||
|
适用细胞 |
部分细胞 |
几乎所有细胞 |
几乎所有细胞 |
内部4种细胞 |
几乎所有细胞 |
部分细胞 |
|
|
转染/感染效率 |
低 |
中 |
高 |
高 |
高 |
低 |
|
|
随机整合 |
是 |
是 |
是 |
否 |
- |
否 |
|
|
生物安全等级 |
BL1 |
BL1 |
BL2 |
BL1 |
BL1 |
BL1 |
|
|
基因装载能力 |
- |
- |
<4-5k |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
阳性率 |
低 |
高 |
高 |
高 |
高 |
低 |
|
|
周期 |
基因合成 |
2-3周 |
2-3周 |
2-3周 |
2-3周 |
2-3周 |
2-3周 |
|
病毒包装 |
- |
- |
1周 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
混合克隆筛选 |
1-2周 |
1-2周 |
1-2周 |
1-2周 |
1-2周 |
1-2周 |
|
|
单克隆筛选 |
>3 周 |
>3 周 |
>3 周 |
可选 |
可选 |
>3 周 |
|
|
合计 |
> 8-10 周 |
> 8-10 周 |
>9-11周 |
5-7 周 |
5-7 周 |
> 8-10 周 |
|
|
工作负荷 |
高 |
中 |
中 |
低 |
低 |
高 |
|


