减脂增肌新靶点-ActRII
发布时间:2025/10/24分类:技术文章来源:科佰生物
背景
激活素 A(Activin A)是转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)超家族的重要成员,是参与过敏、自身免疫性疾病、癌症和其他免疫紊乱疾病的多能因子。ACVR2A(激活素受体2A)和ACVR2B(激活素受体2B)作为Activin A的II型受体,它们在细胞生长、分化和组织修复等多种生理过程中发挥关键作用。这两种跨膜蛋白具有富含半胱氨酸的配体结合域和激酶活性催化结构域,通过与激活素等配体结合,激活下游信号通路如Smad2/3和MAPK,从而调节骨骼肌质量、脂肪代谢、胚胎发育等。由于其在肌肉和脂肪代谢中的重要性,ACVR2A和ACVR2B已成为治疗肌肉萎缩和代谢性疾病的潜在药物靶点。
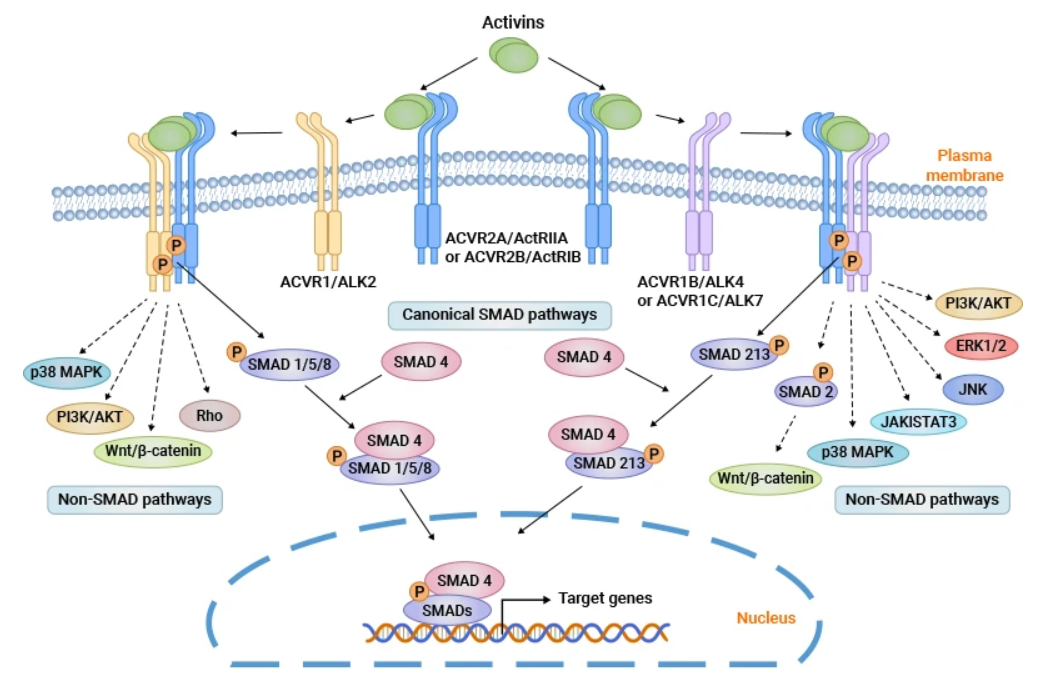
ActRII的结构与功能
Activin A是一种约25 kDa的细胞因子,可通过二硫键与βA和/或 βB 亚基连接形成同源二聚体或异二聚体。Activin A通过两个I型和两个II型受体发出信号,配体结合后,组装最终的受体复合物。I型受体包括激活素受体1A型(或激活素受体样激酶2,ALK2)、激活素受体1B型(或ALK4)和激活素受体1C型(或ALK7)。II型受体(ActRII)分为激活素受体IIA型(ACVR2A)和激活素受体IIB型(ACVR2B)。
激活素A首先结合并促进ActRII的磷酸化,然后招募I型受体形成磷酸化多聚体。激活的受体复合物磷酸化SMAD2 和 SMAD3蛋白,磷酸化后的smad2/3与smad4蛋白结合成三聚体并易位到细胞核中调控相关基因的转录。
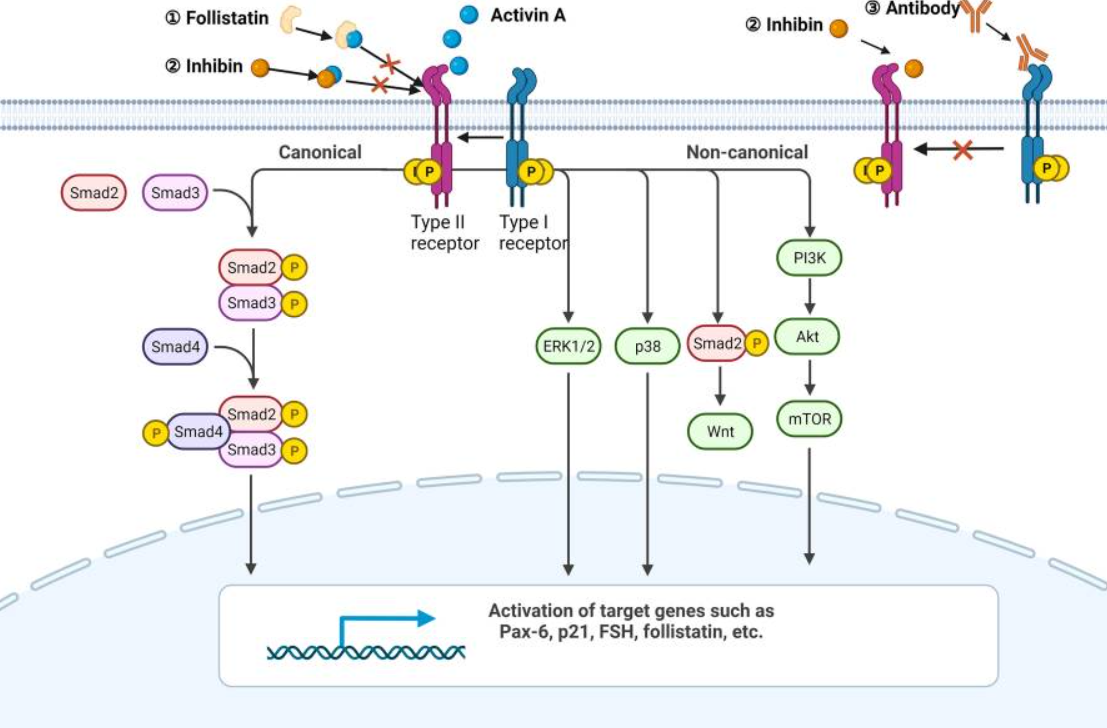
ActRⅡ(激活素Ⅱ型受体(Activin type Ⅱ Receptor))存在于脂肪和肌肉细胞中。在脂肪细胞中,激活素通过ActRⅡ进行脂质存储,阻断该信号通路可促进脂肪代谢。在肌肉细胞中,ActRⅡ受体传导的信号通路能够抑制肌肉生长并导致其萎缩,阻断骨骼肌中的激活素信号可以抑制这种萎缩,并可以促进肌肉质量的增加,帮助肥胖患者在减肥的同时改善身体成分和代谢。
靶向ActRⅡ的药物研发进展
关于ActRⅡ,常用的靶向疗法主要聚焦于融合蛋白和抗体。目前已有两款药物上市,为BMS/默沙东的ActRIIB-Fc融合蛋白药物Luspatercept(治疗地中海贫血)和默沙东开发的ActRIIA-Fc融合蛋白药物Sotatercept(治疗肺动脉高压)。
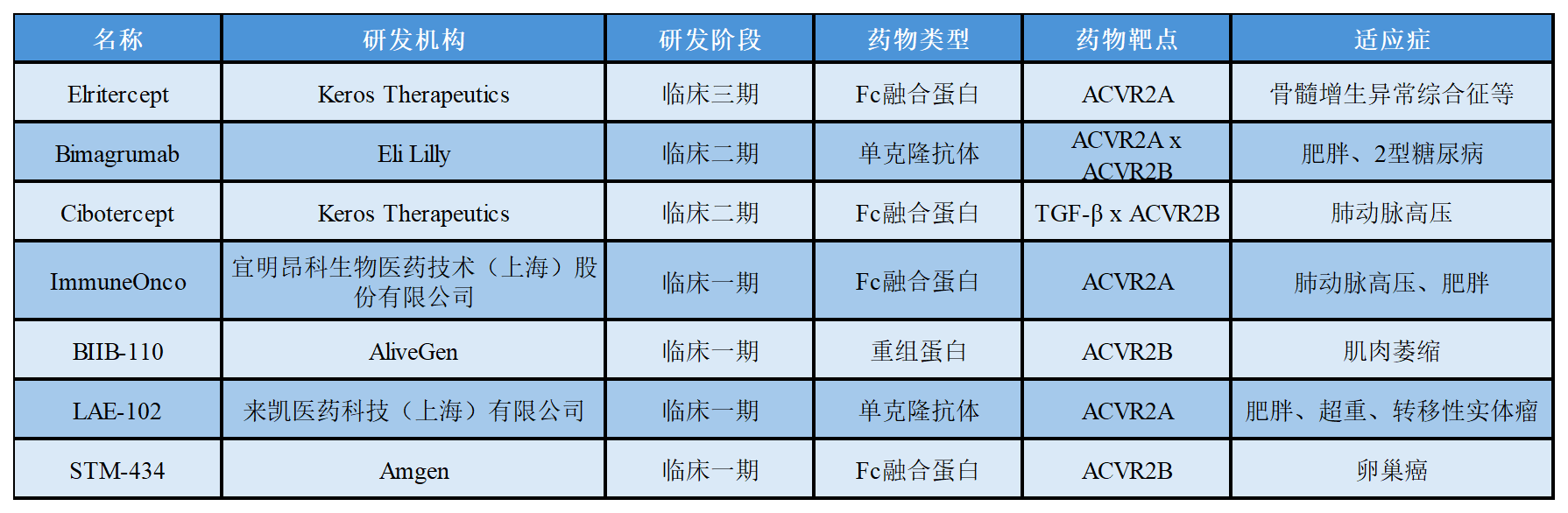
关于ActRⅡ在研的部分药物进展如下表所示:
ActRⅡ的细胞模型
为助力ActRⅡ靶点药物研发,南京科佰开发了Activin A Effector Reporter Cell、ACVR2A CHO、ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell、ACVR2B CHO和ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell细胞筛选模型,部分数据展示如下:
部分数据展示
Activin A Effector Reporter Cell CBP74225
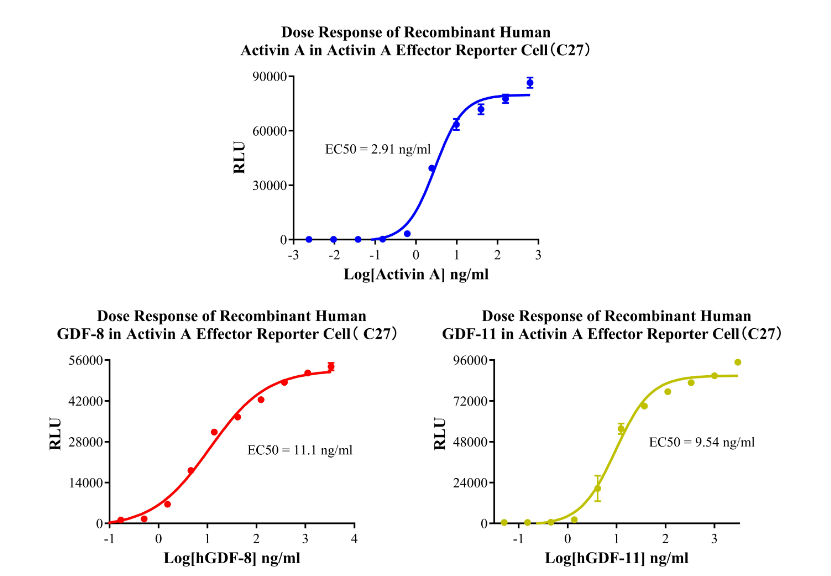
Figure 3.Dose Response of Recombinant Human Activin A in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell( C27).Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-8 in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell( C27).Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-11 in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell(C27).
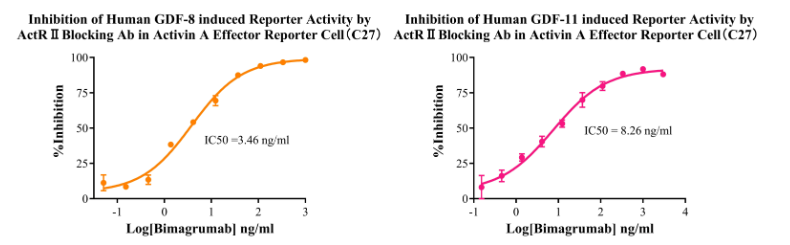
Figure 4. Inhibition of Human GDF-8 induced Reporter Activity by ActR II Blocking Ab in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell(C27). Inhibition of Human GDF-11 induced Reporter Activity by ActR II Blocking Ab in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell(C27).
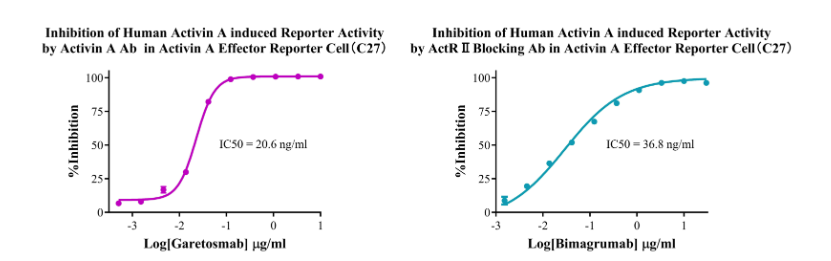
Figure 5. Inhibition of Human Activin A induced Reporter Activity by Activin A Ab in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell(C27). Inhibition of Human Activin A induced Reporter Activity by ActR II Blocking Ab in Activin A Effector Reporter Cell(C27).
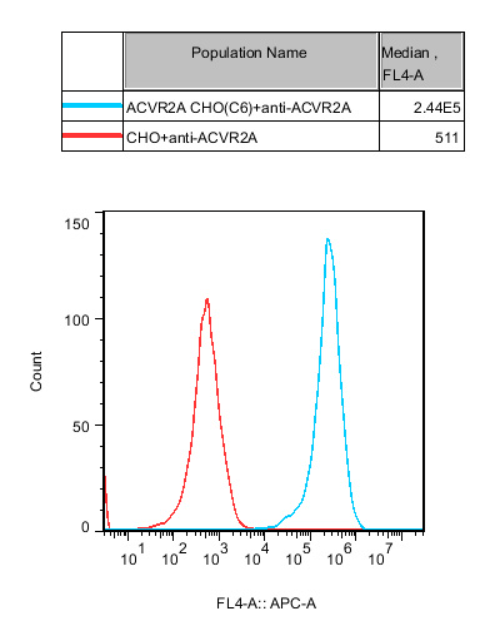
Figure 6. Recombinant ACVR2A CHO stably expressing ACVR2A.
ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell CBP74277
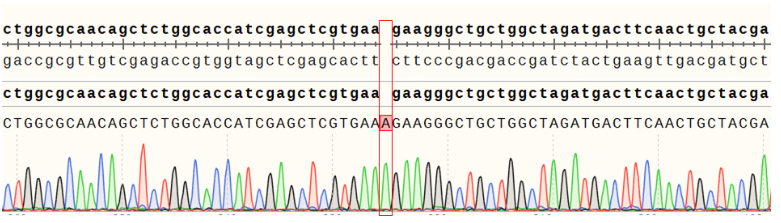
Figure 7.ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell 测序结果 ACVR2B(NM_001106.4): c.221_222insA/ACVR2B:p.K74Kfs*7
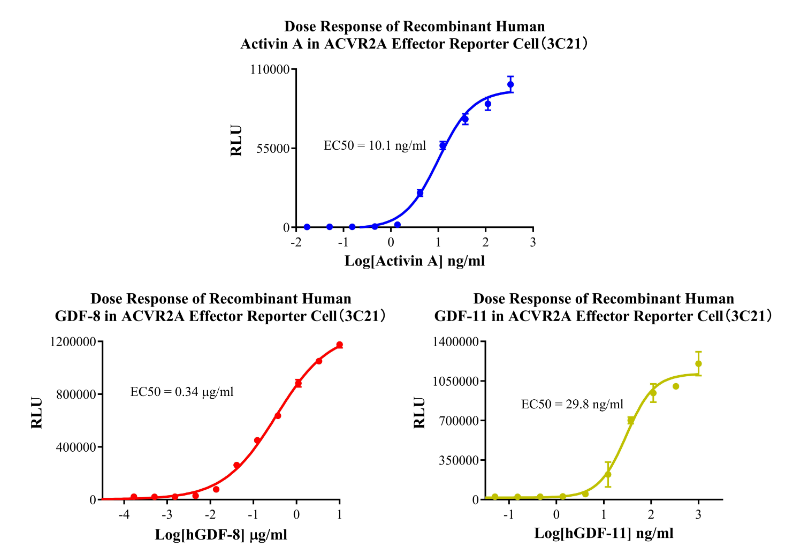
Figure 8. Dose Response of Recombinant Human Activin A in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell(3C21).Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-8 in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell (3C21). Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-11 in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell (3C21).
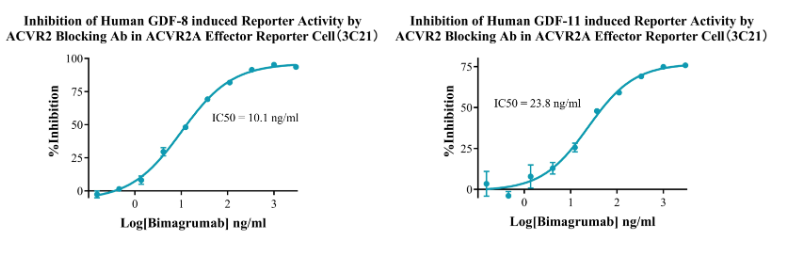
Figure 9. Inhibition of Human GDF-8 induced Reporter Activity by ACVR2 Blocking Ab in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell (3C21).Inhibition of Human GDF-11 induced Reporter Activity by ACVR2 Blocking Ab in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell (3C21).
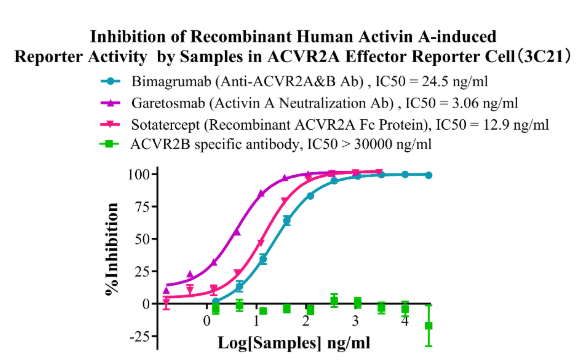
Figure10. Inhibition of Recombinant Human Activin A-induced Reporter Activity by Samples in ACVR2A Effector Reporter Cell (3C21).
ACVR2B CHO CBP74249
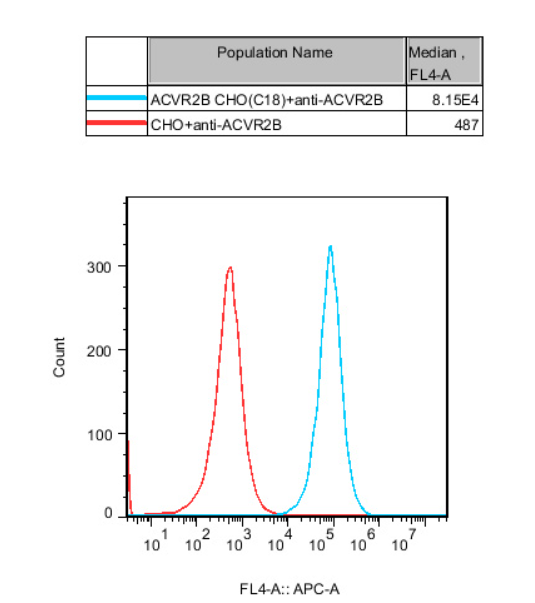
Figure 11.Recombinant ACVR2B CHO stably expressing ACVR2B.
ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell CBP74280
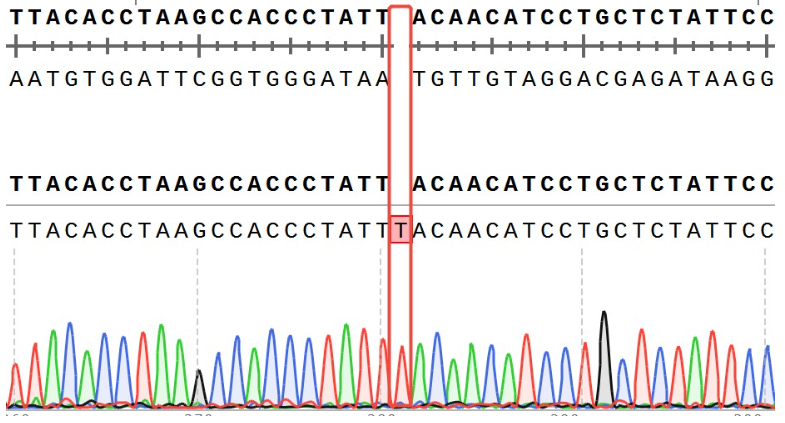
Figure 12. ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell 测序结果 ACVR2A(NM_001616.5): c.409_410insT/ ACVR2A:p.Y137Lfs*76
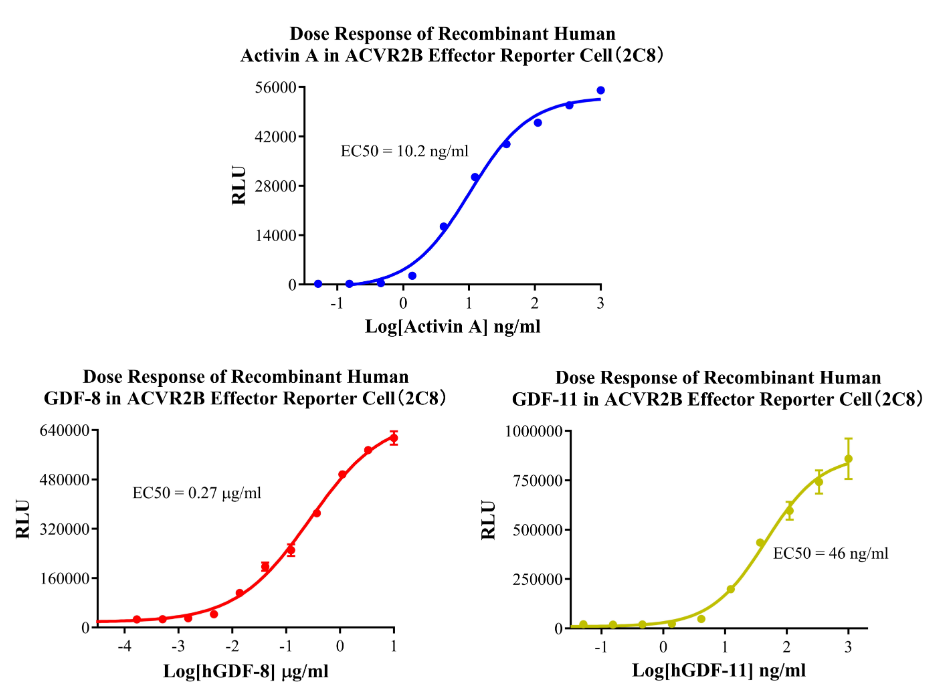
Figure 13.Dose Response of Recombinant Human Activin A in ACVR2B Effector Cell(2C8).Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-8 in ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell(2C8).Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-11 in ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell (2C8).
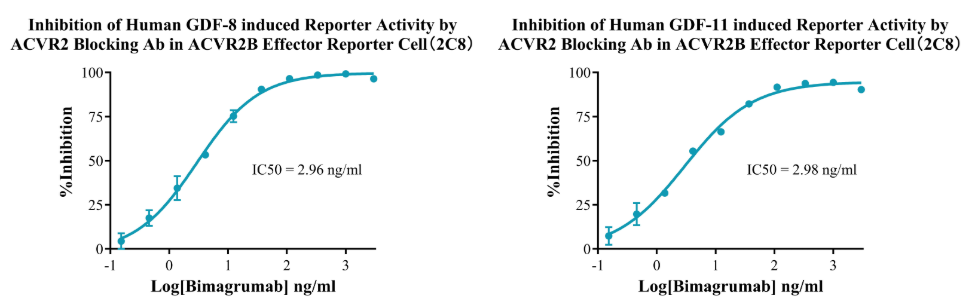
Figure 14. Inhibition of Human GDF-8 induced Reporter Activity byACVR2 Blocking Ab in ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell(2C8). Inhibition of Human GDF-11 induced Reporter Activity by ACVR2 Blocking Ab in ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell(2C8).
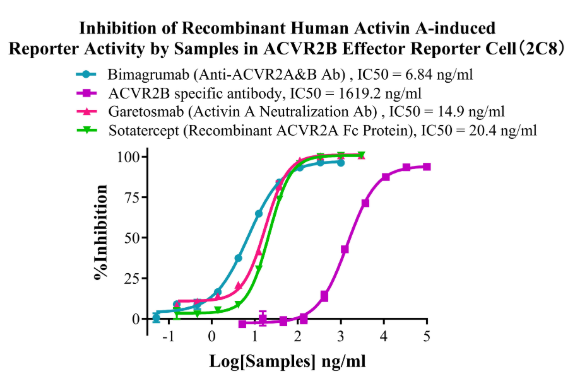
Figure15. Inhibition of Recombinant Human Activin A-induced Reporter Activity by Samples in ACVR2B Effector Reporter Cell (2C8).